#include <gmli.h>
Inheritance diagram for LaGenMatLongInt:
Declaration | |
| LaGenMatLongInt () | |
| LaGenMatLongInt (int m, int n) | |
| LaGenMatLongInt (long int *v, int m, int n, bool row_ordering=false) | |
| LaGenMatLongInt (const LaGenMatLongInt &) | |
| LaGenMatLongInt & | resize (int m, int n) |
| LaGenMatLongInt & | resize (const LaGenMatLongInt &s) |
| virtual | ~LaGenMatLongInt () |
Information Predicates | |
| bool | is_zero () const |
| bool | is_submatrixview () const |
| bool | has_unitstride () const |
| bool | equal_to (const matrix_type &mat) const |
Information | |
| int | size (int d) const |
| int | cols () const |
| int | rows () const |
| int | inc (int d) const |
| int | gdim (int d) const |
| int | start (int d) const |
| int | end (int d) const |
| LaIndex | index (int d) const |
| int | ref_count () const |
| long int * | addr () const |
Access functions | |
| long int & | operator() (int i, int j) |
| long int & | operator() (int i, int j) const |
| LaGenMatLongInt | operator() (const LaIndex &I, const LaIndex &J) |
| LaGenMatLongInt | operator() (const LaIndex &I, const LaIndex &J) const |
| LaGenMatLongInt | row (int k) |
| LaGenMatLongInt | row (int k) const |
| LaGenMatLongInt | col (int k) |
| LaGenMatLongInt | col (int k) const |
Assignments | |
| LaGenMatLongInt & | operator= (long int s) |
| LaGenMatLongInt & | operator= (const LaGenMatLongInt &s) |
| LaGenMatLongInt & | operator+= (long int s) |
| LaGenMatLongInt & | add (long int s) |
| LaGenMatLongInt & | inject (const LaGenMatLongInt &s) |
| LaGenMatLongInt & | copy (const LaGenMatLongInt &s) |
| LaGenMatLongInt | copy () const |
| LaGenMatLongInt & | shallow_assign () |
| LaGenMatLongInt & | ref (const LaGenMatLongInt &s) |
Expensive access functions | |
| matrix_type | repmat (int M, int N) const |
| value_type | trace () const |
| matrix_type | diag () const |
Debugging information | |
| int | shallow () const |
| int | debug () const |
| int | debug (int d) |
| const LaGenMatLongInt & | info () const |
| std::ostream & | Info (std::ostream &s) const |
Matrix type conversions | |
| LaGenMatComplex | to_LaGenMatComplex () const |
| LaGenMatDouble | to_LaGenMatDouble () const |
| LaGenMatFloat | to_LaGenMatFloat () const |
| LaGenMatInt | to_LaGenMatInt () const |
Constructors for elementary matrices | |
| static matrix_type | zeros (int N, int M=0) |
| static matrix_type | ones (int N, int M=0) |
| static matrix_type | eye (int N, int M=0) |
| static matrix_type | rand (int N, int M, value_type low=0, value_type high=1) |
| static matrix_type | from_diag (const matrix_type &vect) |
| static matrix_type | linspace (value_type start, value_type end, int nr_points) |
Public Types | |
| typedef long int | value_type |
| typedef LaGenMatLongInt | matrix_type |
| typedef VectorLongInt | vec_type |
Friends | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &, const LaGenMatLongInt &) |
This is the basic LAPACK++ matrix for long integers. It is a dense (nonsingular) matrix, assumes no special structure or properties.
Unfortunately it is unclear how multiplication of these matrices should be done. Usually they are only created for storing the pivot element ordering.
| typedef long int LaGenMatLongInt::value_type |
The type of the value elements.
Convenience typedef of this class to itself to make common function definitions easier. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5)
| typedef VectorLongInt LaGenMatLongInt::vec_type |
Internal wrapper type; don't use that in an application.
| LaGenMatLongInt::LaGenMatLongInt | ( | ) |
Constructs a null 0x0 matrix.
| LaGenMatLongInt::LaGenMatLongInt | ( | int | m, | |
| int | n | |||
| ) |
Constructs a column-major matrix of size 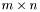 . Matrix elements are NOT initialized!
. Matrix elements are NOT initialized!
| LaGenMatLongInt::LaGenMatLongInt | ( | long int * | v, | |
| int | m, | |||
| int | n, | |||
| bool | row_ordering = false | |||
| ) |
Constructs an 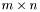 matrix by using the values from the one-dimensional C array
matrix by using the values from the one-dimensional C array v of length m*n.
row_ordering is false, then the data will not be copied but instead the C array will be shared (shallow copy). In that case, you must not delete the C array as long as you use this newly created matrix. Also, if you need a copy (deep copy), construct one matrix A by this constructor, and then copy this content into a second matrix by B.copy(A). On the other hand, if row_ordering is true, then the data will be copied immediately (deep copy).| v | The one-dimensional C array of size m*n whose data should be used. If row_ordering is false, then the data will not be copied but shared (shallow copy). If row_ordering is true, then the data will be copied (deep copy). | |
| m | The number of rows in the new matrix. | |
| n | The number of columns in the new matrix. | |
| row_ordering | If false, then the C array is used in column-order, i.e. the first m elements of v are used as the first column of the matrix, the next m elements are the second column and so on. (This is the default and this is also the internal storage format in order to be compatible with the underlying Fortran subroutines.) If this is true, then the C array is used in row-order, i.e. the first n elements of v are used as the first row of the matrix, the next n elements are the second row and so on. (Internally, this is achieved by allocating a new copy of the array and copying the array into the internal ordering.) |
| LaGenMatLongInt::LaGenMatLongInt | ( | const LaGenMatLongInt & | ) |
Create a new matrix from an existing one by copying.
Watch out! Due to the C++ "named return value optimization" you cannot use this as an alias for copy() when declaring a variable if the right-side is a return value of operator(). More precisely, you cannot write the following:
LaGenMatLongInt x( y(LaIndex(),LaIndex()) ); // erroneous reference copy!
Instead, if the initialization should create a new copy of the right-side matrix, you have to write it this way:
LaGenMatLongInt x( y(LaIndex(),LaIndex()).copy() ); // correct deep-copy
Or this way:
LaGenMatLongInt x;
x = y(LaIndex(),LaIndex()); // correct deep-copy
| virtual LaGenMatLongInt::~LaGenMatLongInt | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Destroy matrix and reclaim vector memory space if this is the only structure using it.
| LaGenMatLongInt& LaGenMatLongInt::resize | ( | int | m, | |
| int | n | |||
| ) |
Resize to a new matrix of size m x n. The element values of the new matrix are uninitialized, even if resizing to a smaller matrix.
| LaGenMatLongInt& LaGenMatLongInt::resize | ( | const LaGenMatLongInt & | s | ) |
Resize to a new matrix of the same size as the given matrix s. The element values of the new matrix are uninitialized, even if resizing to a smaller matrix.
| bool LaGenMatLongInt::is_zero | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if this is an all-zero matrix. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5)
| bool LaGenMatLongInt::is_submatrixview | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns true if this matrix is only a submatrix view of another (larger) matrix. (New in lapackpp-2.4.4)
| bool LaGenMatLongInt::has_unitstride | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns true if this matrix has unit stride.
This is a necessary condition for not being a submatrix view, but it's not sufficient. (New in lapackpp-2.4.4)
| bool LaGenMatLongInt::equal_to | ( | const matrix_type & | mat | ) | const |
Returns true if the given matrix mat is exactly equal to this object. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5)
| int LaGenMatLongInt::size | ( | int | d | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the length n of the dth dimension, i.e. for a M x N matrix, size(0) returns M and size(1) returns N.
| int LaGenMatLongInt::cols | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the number of columns, i.e. for a M x N matrix this returns N. New in lapackpp-2.4.4.
| int LaGenMatLongInt::rows | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the number of rows, i.e. for a M x N matrix this returns M. New in lapackpp-2.4.4.
| int LaGenMatLongInt::inc | ( | int | d | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the distance between memory locations (in terms of number of elements) between consecutive elements along dimension d. For example, if inc(d) returns 1, then elements along the dth dimension are contiguous in memory.
| int LaGenMatLongInt::gdim | ( | int | d | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the global dimensions of the (possibly larger) matrix owning this space. This will only differ from size(d) if the current matrix is actually a submatrix view of some larger matrix.
| int LaGenMatLongInt::start | ( | int | d | ) | const [inline] |
If the memory space used by this matrix is viewed as a linear array, start(d) returns the starting offset of the first element in dimension d. (See LaIndex class.)
| int LaGenMatLongInt::end | ( | int | d | ) | const [inline] |
If the memory space used by this matrix is viewed as a linear array, end(d) returns the starting offset of the last element in dimension d. (See LaIndex class.)
| LaIndex LaGenMatLongInt::index | ( | int | d | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the index specifying this submatrix view in dimension d. (See LaIndex class.) This will only differ from a unit-stride index if the current matrix is actually a submatrix view of some larger matrix.
| int LaGenMatLongInt::ref_count | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the number of data objects which utilize the same (or portions of the same) memory space used by this matrix.
| long int * LaGenMatLongInt::addr | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns the memory address of the first element of the matrix. G.addr() is equivalent to &G(0,0) .
| long int & LaGenMatLongInt::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j | |||
| ) | [inline] |
Returns the 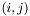 th element of this matrix, with the indices i and j starting at zero (zero-based offset). This means you have
th element of this matrix, with the indices i and j starting at zero (zero-based offset). This means you have
![\[ A_{n\times m} = \left(\begin{array}{ccc} a_{11} & & a_{1m} \\ & \ddots & \\ a_{n1} & & a_{nm} \end{array}\right) \]](form_18.png)
but for accessing the element 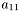 you have to write
you have to write A(0,0).
Optional runtime bounds checking (0<=i<m, 0<=j<n) is set by the compile time macro LA_BOUNDS_CHECK.
| long int & LaGenMatLongInt::operator() | ( | int | i, | |
| int | j | |||
| ) | const [inline] |
Returns the 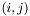 th element of this matrix, with the indices i and j starting at zero (zero-based offset). This means you have
th element of this matrix, with the indices i and j starting at zero (zero-based offset). This means you have
![\[ A_{n\times m} = \left(\begin{array}{ccc} a_{11} & & a_{1m} \\ & \ddots & \\ a_{n1} & & a_{nm} \end{array}\right) \]](form_18.png)
but for accessing the element 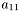 you have to write
you have to write A(0,0).
Optional runtime bounds checking (0<=i<m, 0<=j<n) is set by the compile time macro LA_BOUNDS_CHECK.
| LaGenMatLongInt LaGenMatLongInt::operator() | ( | const LaIndex & | I, | |
| const LaIndex & | J | |||
| ) |
Return a submatrix view specified by the indices I and J. (See LaIndex class.) These indices specify start, increment, and ending offsets, similar to triplet notation of Matlab or Fortran 90. For example, if B is a 10 x 10 matrix, I is (0:2:2) and J is (3:1:4), then B(I,J) denotes the 2 x 2 matrix
![\[ \left(\begin{array}{cc} b_{0,3} & b_{2,3} \\ b_{0,4} & b_{4,4} \end{array}\right) \]](form_20.png)
| LaGenMatLongInt LaGenMatLongInt::operator() | ( | const LaIndex & | I, | |
| const LaIndex & | J | |||
| ) | const |
Return a submatrix view specified by the indices I and J. (See LaIndex class.) These indices specify start, increment, and ending offsets, similar to triplet notation of Matlab or Fortran 90. For example, if B is a 10 x 10 matrix, I is (0:2:2) and J is (3:1:4), then B(I,J) denotes the 2 x 2 matrix
![\[ \left(\begin{array}{cc} b_{0,3} & b_{2,3} \\ b_{0,4} & b_{4,4} \end{array}\right) \]](form_20.png)
| LaGenMatLongInt LaGenMatLongInt::row | ( | int | k | ) |
Returns a submatrix view for the specified row k of this matrix.
The returned object references still the same memory as this object, so if you modify elements, they will appear modified in both objects. (New in lapackpp-2.4.6)
| LaGenMatLongInt LaGenMatLongInt::row | ( | int | k | ) | const |
Returns a submatrix view for the specified row k of this matrix.
The returned object references still the same memory as this object, so if you modify elements, they will appear modified in both objects. (New in lapackpp-2.4.6)
| LaGenMatLongInt LaGenMatLongInt::col | ( | int | k | ) |
Returns a submatrix view for the specified column k of this matrix.
The returned object references still the same memory as this object, so if you modify elements, they will appear modified in both objects. (New in lapackpp-2.4.6)
| LaGenMatLongInt LaGenMatLongInt::col | ( | int | k | ) | const |
Returns a submatrix view for the specified column k of this matrix.
The returned object references still the same memory as this object, so if you modify elements, they will appear modified in both objects. (New in lapackpp-2.4.6)
| LaGenMatLongInt& LaGenMatLongInt::operator= | ( | long int | s | ) |
Set elements of left-hand size to the scalar value s. No new matrix is created, so that if there are other matrices that reference this memory space, they will also be affected.
Reimplemented in LaVectorLongInt.
| LaGenMatLongInt& LaGenMatLongInt::operator= | ( | const LaGenMatLongInt & | s | ) |
Release left-hand side (reclaiming memory space if possible) and copy elements of elements of s. Unline inject(), it does not require conformity, and previous references of left-hand side are unaffected.
This is an alias for copy().
Watch out! Due to the C++ "named return value optimization" you cannot use this as an alias for copy() when declaring a variable if the right-side is a return value of operator(). More precisely, you cannot write the following:
LaGenMatLongInt x = y(LaIndex(),LaIndex()); // erroneous reference copy!
Instead, if the initialization should create a new copy of the right-side matrix, you have to write it this way:
LaGenMatLongInt x = y(LaIndex(),LaIndex()).copy(); // correct deep-copy
Or this way:
LaGenMatLongInt x;
x = y(LaIndex(),LaIndex()); // correct deep-copy
Note: The manual for lapack++-1.1 claimed that this operator would be an alias for ref(), not for copy(), i.e. this operator creates a reference instead of a deep copy. However, since that confused many people, the behaviour was changed so that B=A will now create B as a deep copy instead of a reference. If you want a reference, please write B.ref(A) explicitly.
Reimplemented in LaVectorLongInt.
| LaGenMatLongInt& LaGenMatLongInt::operator+= | ( | long int | s | ) |
Add the scalar value s to elements of left-hand side. No new matrix is created, so that if there are other matrices that reference this memory space, they will also be affected.
| LaGenMatLongInt& LaGenMatLongInt::add | ( | long int | s | ) |
Add the scalar value s to elements of left-hand side. No new matrix is created, so that if there are other matrices that reference this memory space, they will also be affected. (New in lapackpp-2.4.7.)
| LaGenMatLongInt& LaGenMatLongInt::inject | ( | const LaGenMatLongInt & | s | ) |
Copy elements of s into the memory space referenced by the left-hand side, without first releasing it. The effect is that if other matrices share memory with left-hand side, they too will be affected. Note that the size of s must be the same as that of the left-hand side matrix.
s, you should use copy() instead. Reimplemented in LaVectorLongInt.
| LaGenMatLongInt& LaGenMatLongInt::copy | ( | const LaGenMatLongInt & | s | ) |
Release left-hand side (reclaiming memory space if possible) and copy elements of elements of s. Unline inject(), it does not require conformity, and previous references of left-hand side are unaffected.
Reimplemented in LaVectorLongInt.
| LaGenMatLongInt LaGenMatLongInt::copy | ( | ) | const |
Returns a newly allocated matrix that is an element-by-element copy of this matrix.
New in lapackpp-2.5.2
| LaGenMatLongInt & LaGenMatLongInt::shallow_assign | ( | ) | [inline] |
This is an optimization for returning temporary matrices from functions, without copying. The shallow_assign() function essentially sets an internal flag which instructs the X::X(&X) copy constructor to avoid the copying.
| LaGenMatLongInt& LaGenMatLongInt::ref | ( | const LaGenMatLongInt & | s | ) |
Let this matrix reference the given matrix s, so that the given matrix memory s is now referenced by multiple objects (by the given object s and now also by this object). Handle this with care!
This function releases any previously referenced memory of this object.
Reimplemented in LaVectorLongInt.
| matrix_type LaGenMatLongInt::repmat | ( | int | M, | |
| int | N | |||
| ) | const |
Returns a newly allocated large matrix that consists of M-by-N copies of the given matrix. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5.)
| value_type LaGenMatLongInt::trace | ( | ) | const |
Returns the trace, i.e. the sum of all diagonal elements of the matrix. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5)
| matrix_type LaGenMatLongInt::diag | ( | ) | const |
Returns a newly allocated column vector of dimension Nx1 that contains the diagonal of the given matrix. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5)
| int LaGenMatLongInt::shallow | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns global shallow flag
| int LaGenMatLongInt::debug | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Returns global debug flag
| int LaGenMatLongInt::debug | ( | int | d | ) | [inline] |
Set global debug flag
| const LaGenMatLongInt& LaGenMatLongInt::info | ( | ) | const [inline] |
use as in
std::cout << B.info() << std::endl;
this *info_ member is unique in that it really isn't part of the matrix info, just a flag as to how to print it. We've included in this beta release as part of our testing, but we do not expect it to be user accessable.
| std::ostream& LaGenMatLongInt::Info | ( | std::ostream & | s | ) | const [inline] |
Print the matrix info (not the actual elements) to the given ostream.
| LaGenMatComplex LaGenMatLongInt::to_LaGenMatComplex | ( | ) | const |
Convert this matrix to a complex matrix with imaginary part zero.
| LaGenMatDouble LaGenMatLongInt::to_LaGenMatDouble | ( | ) | const |
Convert this matrix to a double (floating-point double precision) matrix.
| LaGenMatFloat LaGenMatLongInt::to_LaGenMatFloat | ( | ) | const |
Convert this matrix to a float (floating-point single precision) matrix.
| LaGenMatInt LaGenMatLongInt::to_LaGenMatInt | ( | ) | const |
Convert this matrix to an int matrix.
| static matrix_type LaGenMatLongInt::zeros | ( | int | N, | |
| int | M = 0 | |||
| ) | [static] |
Returns a newly allocated all-zero matrix of dimension NxN, if M is not given, or NxM if M is given. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5)
| static matrix_type LaGenMatLongInt::ones | ( | int | N, | |
| int | M = 0 | |||
| ) | [static] |
Returns a newly allocated all-one matrix of dimension NxN, if M is not given, or NxM if M is given. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5)
| static matrix_type LaGenMatLongInt::eye | ( | int | N, | |
| int | M = 0 | |||
| ) | [static] |
Returns a newly allocated identity matrix of dimension NxN, if M is not given, or a rectangular matrix NxM if M is given. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5)
| static matrix_type LaGenMatLongInt::rand | ( | int | N, | |
| int | M, | |||
| value_type | low = 0, |
|||
| value_type | high = 1 | |||
| ) | [static] |
Returns a newly allocated matrix of dimension NxM with pseudo-random values. The values are uniformly distributed in the interval (0,1) or, if specified, (low,high). (New in lapackpp-2.4.5)
Note: Since this uses the system's rand() call, the randomness of the values might be questionable -- don't use this if you need really strong random numbers.
| static matrix_type LaGenMatLongInt::from_diag | ( | const matrix_type & | vect | ) | [static] |
Returns a newly allocated diagonal matrix of dimension NxN that has the vector vect of length N on the diagonal. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5)
| static matrix_type LaGenMatLongInt::linspace | ( | value_type | start, | |
| value_type | end, | |||
| int | nr_points | |||
| ) | [static] |
Returns a newly allocated linarly spaced column vector with nr_points elements, between and including start and end. (New in lapackpp-2.4.5.)
| std::ostream& operator<< | ( | std::ostream & | , | |
| const LaGenMatLongInt & | ||||
| ) | [friend] |
Print the matrix to the given output stream. If the matrix info flag is set, then this prints only the matrix info, see LaGenMatDouble::info(). Otherwise all matrix elements are printed.
 1.5.0
1.5.0